Personal Finance Planning and Asset Allocation: A Complete Guide to Secure Your Financial Future
 Personal Finance Planning and Asset Allocation: A Complete Guide to Secure Your Financial Future
Personal Finance Planning and Asset Allocation: A Complete Guide to Secure Your Financial Future
Personal finance planning and asset allocation are the cornerstones of financial success. Whether you’re aiming to build wealth, save for retirement, or create a safety net, having a sound financial plan is essential. This guide will walk you through the steps to manage your money wisely and allocate your assets effectively based on your financial goals and risk appetite.
🧠What is Personal Finance Planning?
Personal finance planning involves managing your income, expenses, savings, investments, and insurance to meet your short-term and long-term goals. It provides a roadmap for financial decision-making and helps you stay prepared for life’s uncertainties.
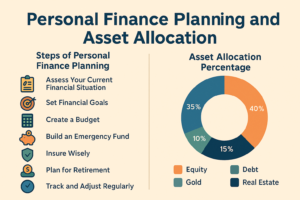
🛠️ 7 Key Steps in Personal Finance Planning
- Analyze Your Current Financial Situation: Track your income, expenses, debts, and assets.
- Set SMART Financial Goals: Make goals Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Build an Emergency Fund: Save 3–6 months of living expenses in a liquid instrument.
- Budget Your Monthly Income: Use the 50/30/20 rule: 50% needs, 30% wants, 20% savings.
- Get the Right Insurance: Life, term, health, and vehicle insurance protect your finances.
- Plan for Retirement Early: Use EPF, PPF, NPS, or mutual funds to grow retirement wealth.
- Review & Adjust Regularly: Revisit your financial plan at least once a year.
💼 What is Asset Allocation?
Asset allocation is the process of distributing your investment across various asset classes—equity, debt, gold, real estate, and cash—based on your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial goals.
📊 Recommended Asset Allocation Based on Risk Profile
| Asset Class | Conservative (Low Risk) | Balanced (Moderate Risk) | Aggressive (High Risk) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equity (Stocks, Mutual Funds) | 20% | 50% | 70% |
| Debt (Bonds, PPF, FDs) | 50% | 30% | 15% |
| Gold (SGBs, Gold ETFs) | 10% | 10% | 5% |
| Real Estate | 15% | 5% | 5% |
| Cash/Liquid Assets | 5% | 5% | 5% |
🎯 Rule of Thumb: 100 Minus Age
A simple asset allocation strategy is the “100 minus age” rule, which suggests allocating a percentage of your portfolio to equities by subtracting your age from 100.
Example: A 30-year-old should invest 70% in equities and the rest in debt and other safer assets.
🧮 Helpful Tools
- SIP Calculators – Plan monthly investments
- Home Loan Calculators – Optimize EMI planning
- Retirement Calculators – Forecast your future needs
🛡️Risk Management & Diversification
Never put all your money into one asset. Diversify your portfolio to reduce risk. Diversification ensures that even if one asset class underperforms, your overall portfolio stays balanced.
✅ Final Thoughts
Personal finance planning and asset allocation are not one-time tasks—they’re continuous processes. Start early, review often, and align your financial decisions with your life goals. With the right strategy and discipline, you can achieve financial independence and security.
📈 FAQs
Q1. What is the best asset allocation strategy?
Answer: The best strategy depends on your age, income, goals, and risk appetite. Start with “100 minus age” as a base.
Q2. Can I change my asset allocation later?
Answer: Absolutely! It’s recommended to review and rebalance your portfolio annually.
Q3. How much should I keep in my emergency fund?
Answer: Ideally, 3–6 months of essential expenses in a liquid fund.

 Personal Finance Planning and Asset Allocation: A Complete Guide to Secure Your Financial Future
Personal Finance Planning and Asset Allocation: A Complete Guide to Secure Your Financial Future